
A vulnerability to events that impact broad economic outcomes is called systematic risk. These outcomes include aggregate income as well total resource holdings and market returns. Systemic risk can vary widely from one country. There are three basic types of systematic risk. These are market and inflation risks, as well as negative externalities. Let's examine each one in turn. Consider how systematic threats affect your investments, and your portfolio.
Market risk
Investors who invest in stocks or bonds face systemic risk. Also known as market risk. This is due to changes in the prices of the underlying assets and the underlying markets. Large investors that hold large quantities of securities can increase this risk in the financial markets. Investors face market risk as well as credit and other risks. This refers to uncertainty regarding a company’s prospects, credit worthiness, or ability to repay debt.
Inflation risk
Inflation is a risk that can have serious consequences for a person's financial security. Inflation decreases the purchasing power and prices rise. Inflation is especially detrimental to fixed income investments such as bonds, which generally have a fixed interest rate and a high purchasing power. There are many financial tools that investors have access to to reduce the risk of inflation. Here are some examples. -Inflation periods are a good time to increase your income in order to reduce systematic risk
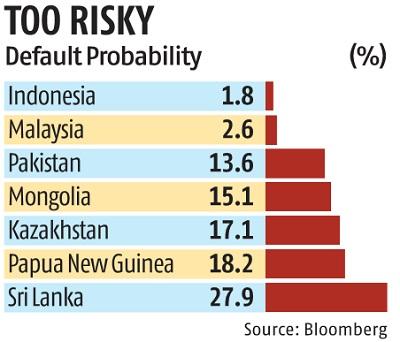
Risks to purchasing power
Inflation risk, also known as purchasing power risk, can lead to your investment portfolio losing its value over time. This is because inflation reduces money's purchasing power. This means that the same amount money can buy fewer goods and services. This can make your spending more difficult. Purchasing power risk is particularly problematic for fixed income securities, since these investments are valued in nominal terms. Equity shares, however, are less susceptible to purchasing power risks.
Negative externalities
There are many examples in economics of negative externalities. Light pollution is one example. When street lights are turned on, they affect the surrounding neighborhoods, but there's no way to compensate those affected. You can also consider the impact of production on the environment. One example is that the cost of manufacturing products can create noise that is disruptive to nearby residents. Consumers don't have to compensate for this noise. Negative externalities are often caused by production and consumption.
Increasing capital
There is a positive correlation between the amount of risk capital a firm takes and its expected returns. If the firm has too little risk capital, however, this correlation can be negative. This is because bank stocks can be undervalued by capital requirements. However, these effects cannot be completely avoided. It is important for policymakers to consider other policies in addition to increasing capital requirements to avoid such negative effects. This paper examines two main policy options.
Diversification
Diversification, like its name implies, is a method to manage both systematic and unsystematic risks. Systematic risk is a risk that is not distributed in the stock market. Unlike unsystematic risk, which can affect the entire market, systematic risk is limited to one specific security or portfolio. The best way to minimize systematic risk is to diversify. Diversification reduces systemic risk by narrowing the range of possible outcomes and increasing the diversity within a portfolio.
Measurement
Systematic risk refers to the possibility of financial system failures due the system's characteristics. Due to its enormous costs, it is imperative that financial institutions are properly regulated macroprudentially. This paper presents a novel approach to measure systemic risk. This analysis is particularly useful for policymakers who want to maintain stability in the financial system and reduce its costs. The methodology is based statistical methods and can be applied in any type of financial systems.
FAQ
Six Sigma is so well-known.
Six Sigma is easy to use and can lead to significant improvements. Six Sigma provides a framework to measure improvements and allows companies to focus on the most important things.
What is the role of a manager in a company?
Different industries have different roles for managers.
A manager is generally responsible for overseeing the day to day operations of a company.
He/she will ensure that the company fulfills its financial obligations.
He/she makes sure that employees adhere to the rules and regulations as well as quality standards.
He/she plans and oversees marketing campaigns.
What's the difference between Six Sigma and TQM?
The main difference in these two quality management tools lies in the fact that six sigma is focused on eliminating defects and total quality management (TQM), emphasizes improving processes and reducing costs.
Six Sigma is an approach for continuous improvement. It emphasizes the elimination and improvement of defects using statistical methods, such as control charts, P-charts and Pareto analysis.
The goal of this method is to reduce variation in product output. This is done by identifying root causes and rectifying them.
Total quality management involves measuring and monitoring all aspects of the organization. It also includes training employees to improve performance.
It is often used to increase productivity.
What is TQM?
The industrial revolution led to the birth and growth of the quality movement. Manufacturing companies realized they couldn't compete solely on price. If they wanted to stay competitive, they needed to improve their quality and efficiency.
Management realized the need to improve and created Total Quality Management, which focused on improving all aspects within an organization's performance. It included continuous improvement processes, employee involvement, and customer satisfaction.
Why is it so important for companies that they use project management techniques
Project management techniques ensure that projects run smoothly while meeting deadlines.
Because most businesses depend heavily on project work to produce goods or services,
Companies must manage these projects effectively and efficiently.
Companies could lose their time, reputation, and money without effective project management.
Statistics
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do you implement a Quality Management Plan (QMP)?
QMP, which was introduced by ISO 9001:2008, is a systematic approach to improving products, services, and processes through continuous improvement. It is about how to continually measure, analyze, control, improve, and maintain customer satisfaction.
QMP stands for Quality Management Process. It is used to guarantee good business performance. The QMP aims to improve the process of production, service delivery, and customer relationship. QMPs should cover all three dimensions - Products, Processes, and Services. A "Process" QMP is one that only includes one aspect. When the QMP focuses on a Product/Service, it is known as a "Product" QMP. QMP stands for Customer Relationships.
When implementing a QMP, there are two main elements: Scope and Strategy. These elements can be defined as follows.
Scope: This describes the scope and duration for the QMP. If your organization wishes to implement a QMP lasting six months, the scope will determine the activities during the first six month.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP has five phases: Planning (Design, Development), Implementation (Implementation), and Maintenance. Each phase is described below:
Planning: This stage identifies and prioritizes the QMP's objectives. Every stakeholder involved in the project is consulted to determine their expectations and needs. Next, you will need to identify the objectives and priorities. The strategy for achieving them is developed.
Design: The design stage involves the development of vision, mission strategies, tactics, and strategies that will allow for successful implementation. These strategies can be implemented through the creation of detailed plans.
Development: Here the development team works toward building the necessary resources and capabilities to support the successful implementation.
Implementation is the actual implementation of QMP according to the plans.
Maintenance: It is an ongoing process that maintains the QMP over time.
In addition, several additional items must be included in the QMP:
Participation by Stakeholders is essential for the QMP's continued success. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. In other words, they must understand the motivation for initiating the project and the expectations of the outcome.
Time Frame: The time frame of the QMP is very critical. The simplest version can be used if the QMP is only being implemented for a short time. For a long-term commitment you may need more complicated versions.
Cost Estimation: Another important component of the QMP is cost estimation. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. It is therefore important to calculate the cost before you start the QMP.
QMPs are more than just documents. They can also be updated as needed. It is constantly changing as the company changes. So, it should be reviewed periodically to make sure that it still meets the needs of the organization.