California's Air Resource Board (or Air Resource Board) is a state agency that sets air quality standards. It regulates emissions from stationary sources and mobile sources, holds monthly public meetings to monitor progress and has a legal office that provides assistance to air quality management districts. The CARB Board members are from many backgrounds. The organization's mission protects public health by encouraging the use of the most advanced technologies to reduce indoor air pollution. The organization's members are drawn from many sectors and come with diverse backgrounds including academia and government.
California's state air resource board is responsible in setting health-based standards for air quality.
CARB, or the California Air Resources Board is responsible to set health-based air quality standards. Its primary goals are to safeguard the public's health as well as protect our environment. CARB helps California residents avoid harmful air pollutants and respiratory illnesses by setting air quality standards. There are 16 members to the California Air Resources Board. The majority are appointed by the Governor and confirmed by the state Senate. They are composed of six local air districts as well as four experts who have an impact on air quality regulations. California Air Resources Board rules are based upon research, sound science and significant technological advances.
California has established aggressive pollution control policies and pollution reduction programmes to meet these standards. One of the most important aspects of these programs was the implementation of policies that target on-road mobile emission. But the overall program success came from a comprehensive approach, reducing air pollution from all major sources. This applies to power plants, factories and homes. California regulates not only air pollution but also smog.

It regulates the emissions from mobile sources.
California's Air resource board can regulate mobile sources. These sources contribute over 50 percent to the nation's air pollution. These emissions are regulated by Title II under the Clean Air Act. During the past decade, CARB has been working on a comprehensive strategy for mobile sources. The Mobile Source Strategy is a comprehensive strategy that aims at reducing smog-forming pollutants by 80 percent, diesel emissions by 45 per cent, greenhouse gases and petroleum consumption to 50 percent.
This plan aims at protecting public health by reducing harmful chemical emissions. It requires vehicle manufacturers that they produce clean engines, and fuels by the deadline. As a result, the EPA adopted stricter standards in the 1970s for mobile sources. It has also implemented stricter regulations regarding pollutants and diesel particulate matters to regulate mobile source emissions.
It holds monthly meetings for the public to review progress
The Air Resources Board (ISO) is an independent body that meets monthly in order to discuss air quality issues and other state-related matters. The governor appoints them and the Senate confirms them. They include representatives from six local air districts, four experts in fields that shape air quality rules, and two public members. One member is the chair of the board. Two non-voting members are also appointed by the Assembly/Senate to oversee Legislative oversight. The members serve staggered six-year terms.
California Air Resources Board has adopted a blueprint to guide its community air protection program. The agency will work together with community members and air districts to improve the air quality in areas that have suffered from multiple forms of pollution. This new approach is the direct result of Assembly Bill 617 which Governor Brown signed in July 2017. The Board chose the first ten communities for the Community Air Protection Program. This program will be expanded to other areas.
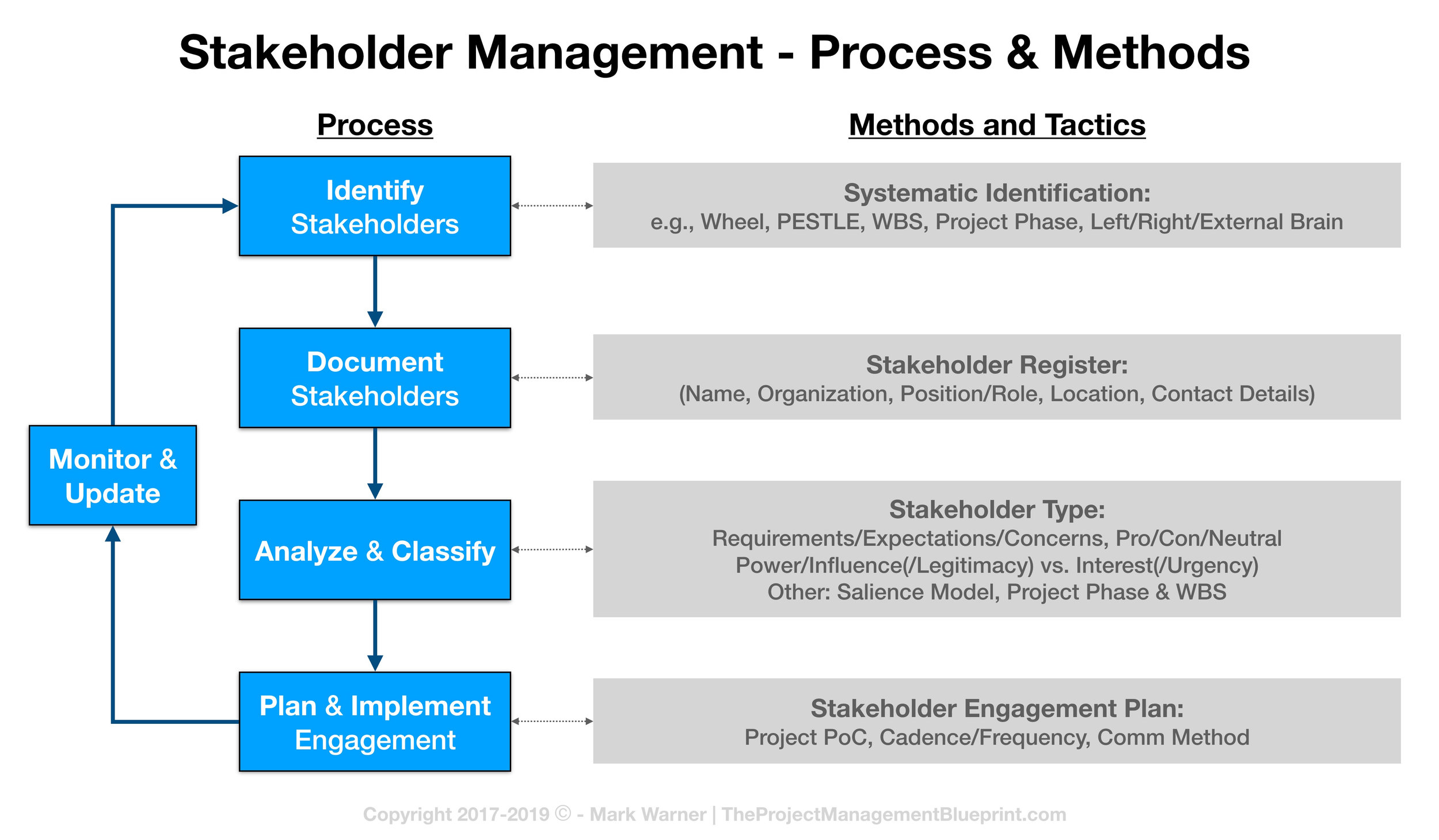
It has a legal office that provides legal assistance to local air quality management districts
The air resource board has a legal office to provide assistance to local air quality management districts. The lawyers are responsible for compliance certifications as well as reporting requirements. In addition, they provide defense to federal and state authorities when they open investigations. A lawyer who specializes in air quality law can help you with any kind of legal matter, including a lawsuit or a grievance. It is crucial to get in touch with a lawyer quickly if there are any problems with your project.
FAQ
What is the meaning of "project management?"
That is the management of all activities associated with a project.
These include planning the scope and identifying the needs, creating the budget, organizing the team, scheduling the work and monitoring progress. Finally, we close down the project.
Why does it sometimes seem so difficult to make good business decisions?
Complex business systems have many moving parts. The people who run them must juggle multiple priorities at once while also dealing with uncertainty and complexity.
Understanding how these factors impact the whole system is key to making informed decisions.
This requires you to think about the purpose and function of each component. Then, you need to think about how these pieces interact with one another.
Also, you should ask yourself if there have been any assumptions in your past behavior. If you don't have any, it may be time to revisit them.
Asking for assistance from someone else is a good idea if you are still having trouble. You may be able to see things from a different perspective than you are and gain insight that can help you find a solution.
What role does a manager have in a company's success?
There are many roles that a manager can play in different industries.
The manager oversees the day-to-day activities of a company.
He/she ensures the company meets its financial commitments and produces goods/services that customers demand.
He/she makes sure that employees adhere to the rules and regulations as well as quality standards.
He/she designs new products or services and manages marketing campaigns.
What's the difference between leadership & management?
Leadership is about inspiring others. Management is all about controlling others.
Leaders inspire others, managers direct them.
A leader motivates people and keeps them on task.
A leader develops people; a manager manages people.
Statistics
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It is about how to continually measure, analyze, control, improve, and maintain customer satisfaction.
The QMP is a standard method used to ensure good business performance. QMP is a standard method that improves the production process, service delivery, customer relationship, and overall business performance. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. If the QMP focuses on one aspect, it is called "Process." QMP. QMPs that focus on a Product/Service are known as "Product" QMPs. And when the QMP concentrates on Customer Relationships, it is called "Customer" QMP.
When implementing a QMP, there are two main elements: Scope and Strategy. These are the following:
Scope: This determines the scope and duration of the QMP. If your organization wishes to implement a QMP lasting six months, the scope will determine the activities during the first six month.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken to achieve the goals set out in the scope.
A typical QMP consists of 5 phases: Planning, Design, Development, Implementation, and Maintenance. Each phase is described below:
Planning: This stage determines the QMP goals and prioritizes them. To get to know the expectations and requirements, all stakeholders are consulted. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage involves the creation of the vision, mission, strategies and tactics necessary to implement the QMP successfully. These strategies can be implemented through the creation of detailed plans.
Development: Here, the development team works towards building the necessary capabilities and resources to support the implementation of the QMP successfully.
Implementation involves the actual implementation using the planned strategies.
Maintenance: This is an ongoing process to maintain the QMP over time.
Additional items must be included in QMP.
Stakeholder Engagement: It is crucial for the QMP to be a success. They should be involved in planning, design, development and implementation of the QMP.
Project Initiation: It is essential to have a clear understanding about the problem and the solution before you can initiate a project. In other words, the initiator needs to know why they want to do something and what they expect from the outcome.
Time Frame: The time frame of the QMP is very critical. You can use a simplified version if you are only going to be using the QMP for short periods. However, if you have a long-term commitment, you may require more elaborate versions.
Cost Estimation - Cost estimation is an important part of the QMP. You cannot plan without knowing how much money you will spend. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
QMPs are not just a written document. They should be a living document. It evolves as the company grows and changes. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.